Understanding Picky Eating Behaviors and Food Acceptance
3 min read • By: Gerber Medical Hub

Quick Summary
Learn about food acceptance and picky eating, including preferences, behaviors, and observations.
Table of contents
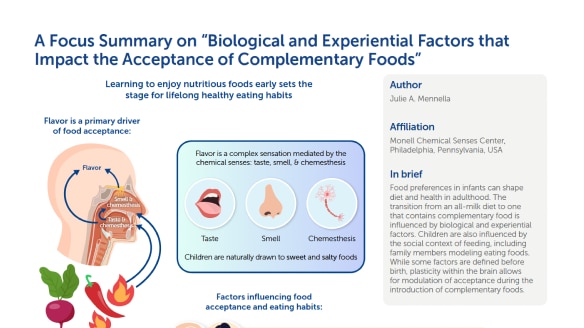
What is Food Acceptance?
When talking about food acceptance and picky eating, we are referring to the preferences and behaviors children have towards consuming different types of food (Taylor 2015). Food acceptance refers to the willingness to try and consume a variety of foods (Meiselman 2003), while picky eating can refer behaviors resulting in the selective and often limited food choices made by children (Samuel 2018, Taylor 2019). It involves being hesitant or refusing to eat certain foods, often due to normal childhood development but can also be due to sensory issues, aversions, or strong preferences. Picky eating can be observed in both children and adults and can impact their nutritional intake and overall well-being.
When Does Picky Eating Start?
Picky eating behaviors emerge at various ages, but it is most observed in early childhood. It typically starts around the age of 2 to 3 years when children become more independent and assert their preferences (Lavin 2001, Mascola 2010, Nicklaus 2019, Taylor 2019). This is a normal developmental stage in which the behavior is transient (Cardona Cano 2015, Diamantis 2023) and seems to resolve spontaneously through exposure to a wide range of foods, by being more socially active through school, and building independence and autonomy along with a wider range of role modeling from peers (Taylor 2019).
What Are the Rates Among Children?
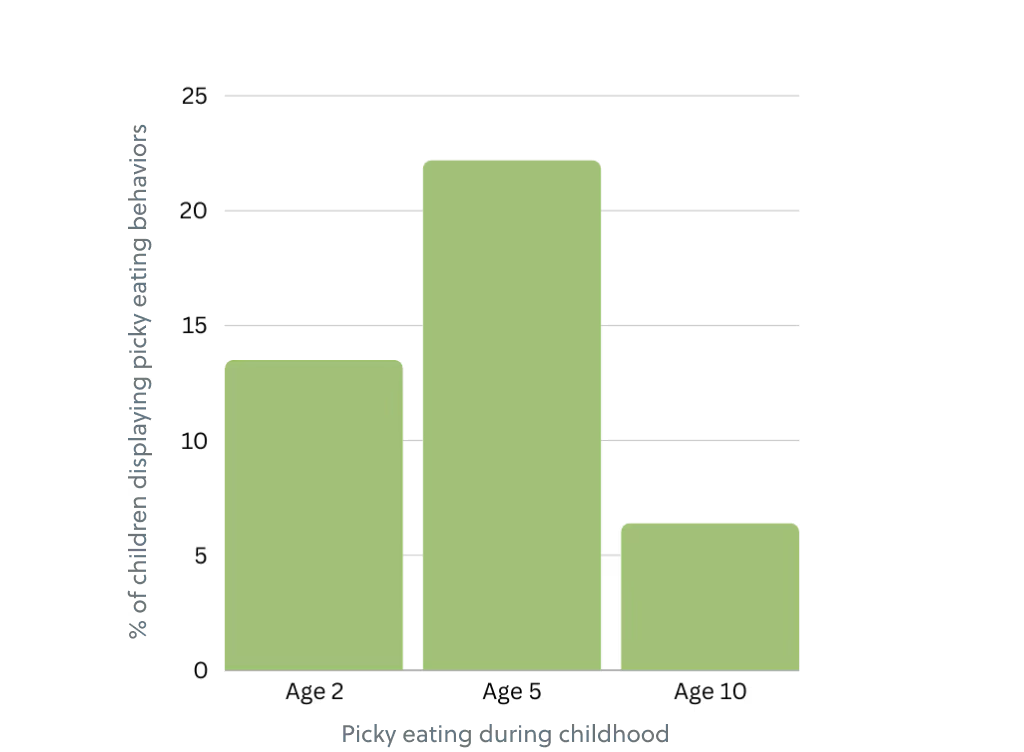
Picky eating is common during childhood (a behavior displayed by approximately 25-33% of children) (Romeo 2023, Samuel 2018). Bourne et al. (2023) found that 13.5% of children displayed picky eating behaviors at age 2, 22.2% at age 5, and 6.4% at age 10 based on parent report and therefore rooted in observations and perceptions of parents and carers.
However, picky eating behaviors left unchecked or that increase instead of resolve may impart poor diet quality (Taylor 2019) and are associated with lower intake frequencies of various healthy foods once a young adult (Pereboom 2023). Therefore, it is important to address picky eating to promote healthy eating behaviors in children early on.
How to support Parents & Caregivers
Health professionals can help parents understand picky eating, discerning what is “normal” versus cause for concern. Having a conversation with parents or caregivers about how children can accept a variety of nutritious foods early can be a helpful practice. Below are resources to support conversations with parents and caregivers:
- Feeding Matters: Picky Eating: Just a Phase or Cause for Greater Concern?
- AAP: 10 Tips for Parents During the Picky Eating Phase
- CDC: Playful Activities for Children Displaying Picky Eating Behavior